Beyond Bug Fixes: How Upstream Investment Drives Success
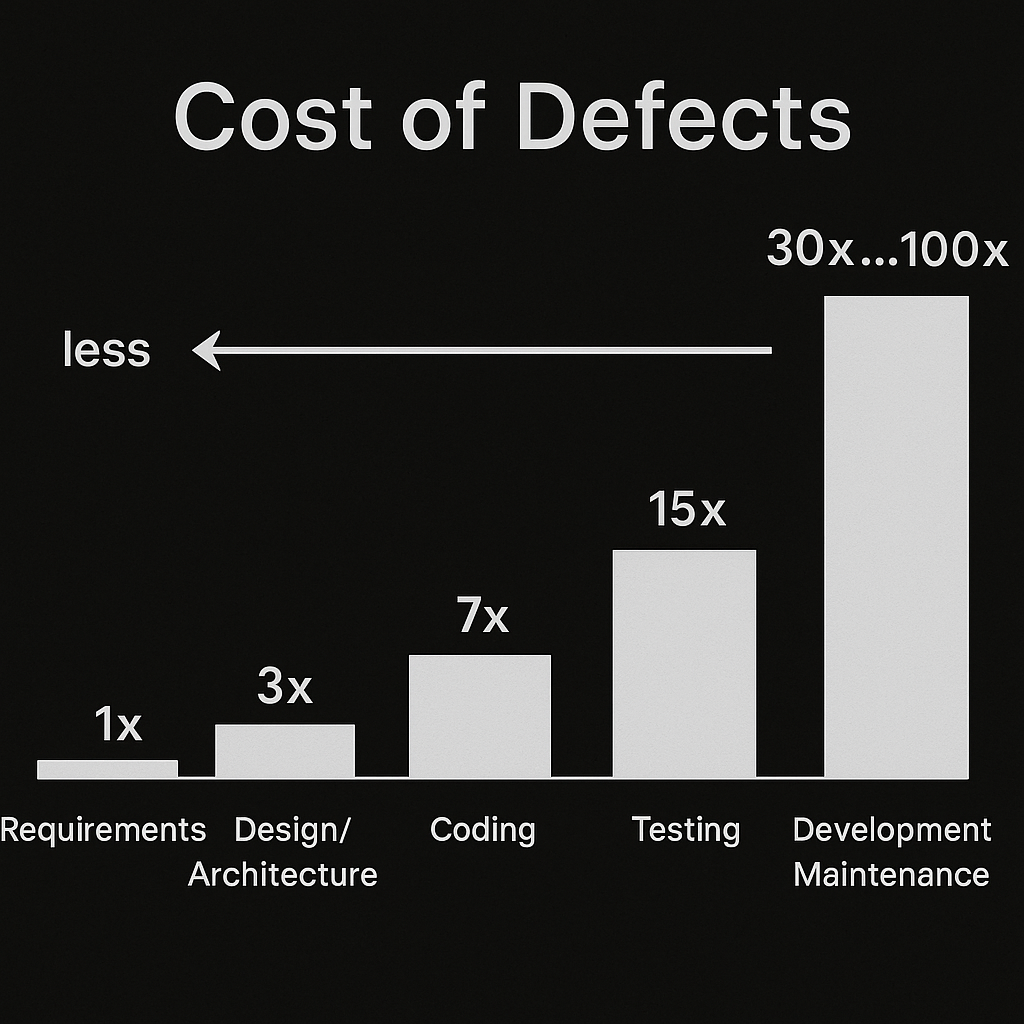
When the cost of fixing a bug discovered during the design phase is set to 1, the cost increases to approximately 6 times during implementation, 15 times during testing, and up to 100 times after product release
—This is a widely cited figure in the software development industry.
While questions have been raised about the authenticity of the IBM Systems Sciences Institute research that supposedly originated these numbers, anyone with experience in large-scale team system development can intuitively understand how bug fix costs increase dramatically as discovery is delayed.
As bug discovery is delayed, the scope of impact from fixes expands, requiring additional work such as retesting, redesign, and user support. Bug fixes in production environments carry additional risks including service outages and loss of customer trust.
The Cost Cascade Effect—Insights from Shopify App Development
The dramatic variation in bug fix costs across development phases stems from "impact scope" and "rework costs." This phenomenon is particularly evident in Shopify app development.
Consider developing a Shopify app that "receives order data webhooks and integrates them with internal systems."
Design Phase (Cost: 1)
At this stage, if we correctly identify during requirements definition that "gift messages included in orders must also be part of the integration," we simply need to include that field in our data structure. The correction cost is minimal.
Implementation Phase (Cost: ~6x)
Discovering that "gift messages are missing" after implementation has progressed requires modifications to API response handling, validation logic, and test code. The number of affected files increases, making impact assessment and coordination time-consuming.
Testing Phase (Cost: ~15x)
When QA finally reveals that "gift messages aren't being integrated for some orders," we need bug investigation, data reprocessing, and client coordination. Including specification confirmation, code fixes, and test re-execution, this requires days of resources.
Post-Release (Cost: Up to 100x)
When this bug is discovered in production through customer complaints, we face data correction for already processed transactions, impact analysis, potential system downtime, and emergency patches. Brand trust impact and human response costs make this the most expensive fix phase.
This illustrates how small oversights in early stages compound into significant costs over time—the essence of bug fix economics. For Shopify apps that integrate with other systems, upstream precision becomes even more critical.
Leverage Effects of Upstream Investment
Achieving early bug detection and resolution requires resource investment in upstream processes like requirements definition and design. Quality improvements in these phases reduce rework in subsequent development and testing phases, enhancing overall development efficiency.
However, upstream investments often get undervalued because their benefits aren't immediately visible. In reality, experienced directors (who have led similar projects) and architects (who combine experience with theoretical knowledge) leading upstream processes improve overall project success rates and deliver long-term cost reductions.
Downstream Challenges and Solutions
As development progresses, specification details become clearer and new issues or bugs inevitably emerge. Since completely preventing this is impossible, we need systems that can respond flexibly in downstream phases.
This requires building development processes that maintain quality while enabling rapid response—through continuous code reviews, automated testing, and CI/CD pipeline implementation.
Director Value and ROI
When experienced directors and architects engage from project inception, they can prevent potential risks and bugs before they materialize. Their expertise and experience provide value across multiple dimensions: problem identification during design, appropriate technology selection, and inter-team coordination.
This results in improved project quality, cost reduction, and schedule adherence—outcomes that justify director compensation levels.
Consider a concrete example: if bug fixes during testing average 3 days, design-phase fixes should require only 0.2 days (about 1.6 hours). Even if a senior director's hourly rate is 3 times that of a test engineer, the 15x cost difference means design-phase investment delivers 5x effectiveness.
Success Visibility and Evaluation Challenges
Success stories like early bug detection and risk prevention are difficult to evaluate because their value remains invisible when problems don't manifest. However, recognizing that these "non-events" themselves represent successful outcomes from appropriate upstream investment and process improvements is crucial.
This requires establishing systems to quantitatively record, analyze, and share quality metrics, risk assessments, and improvement activity results across project phases among stakeholders.
Preventing Wasted Time Through Bug Prevention
Early bug detection and resolution are key to cost reduction and quality improvement in software development. Through appropriate upstream investment, experienced talent utilization, and flexible development process construction, we can increase project success probability. Additionally, success case visualization and evaluation enable continuous improvement and organizational maturity enhancement.
In practical project terms, implementing Proof of Concepts (PoCs) for critical functions before project start, prototype development for user department alignment, and enhanced requirements definition and design phases (senior member assignment, robust review processes) represent strategic investments that increase project success probability while actually reducing total project costs.
